Plastic injection molding is a crucial process in the manufacturing industry, particularly for producing plastic parts and products in large quantities. Below is an overview of its basics, including how it works and its applications.
How Plastic Injection Molding Works
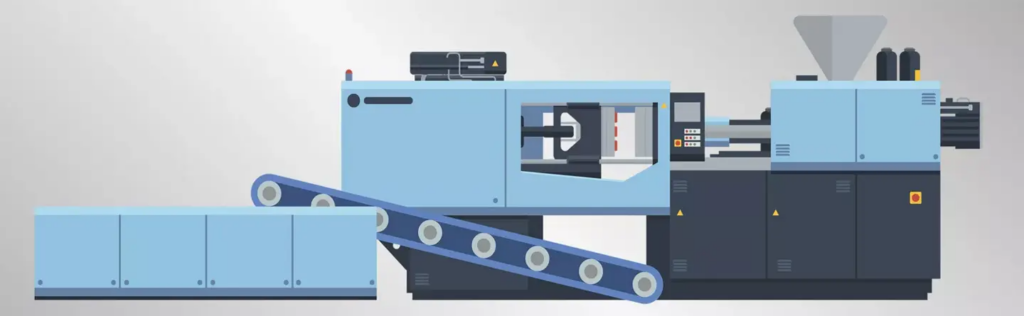
Plastic injection molding involves several key steps:
- Plasticizing and Injection:
- Plastic raw materials undergo preprocessing such as drying, screening, and mixing to become suitable for injection molding.
- In the heating barrel of the injection machine, the plastic melts and plasticizes under heat, forming a uniform molten state.
- The plasticized material is then pushed into the nozzle of the injection machine by the plunger or screw.
- When sufficient plastic accumulates in the nozzle, it is injected into the pouring system of the mold under the driving force of the injection machine.
- Mold Filling:
- Under the pressure of the injection machine, the molten plastic flows into the mold cavity and fills it completely.
- During this process, the plastic continues to plasticize and melt under pressure and temperature.
- Simultaneously, the mold’s cooling system begins to remove heat from the mold through cooling channels or media, enabling the plastic to cool and solidify quickly in the cavity.
- Mold Opening and Release:
- Once the plastic has cooled and hardened in the mold cavity, the mold is opened.
- The molded plastic product is then pushed out or removed from the mold cavity.
- The mold is closed again, ready for the next injection molding cycle.
- Auxiliary Actions:
- Other actions, such as mold exhaust, ejector mechanism adjustment, and mold temperature control, are also crucial to ensure product quality and production stability.
Applications of Plastic Injection Molding
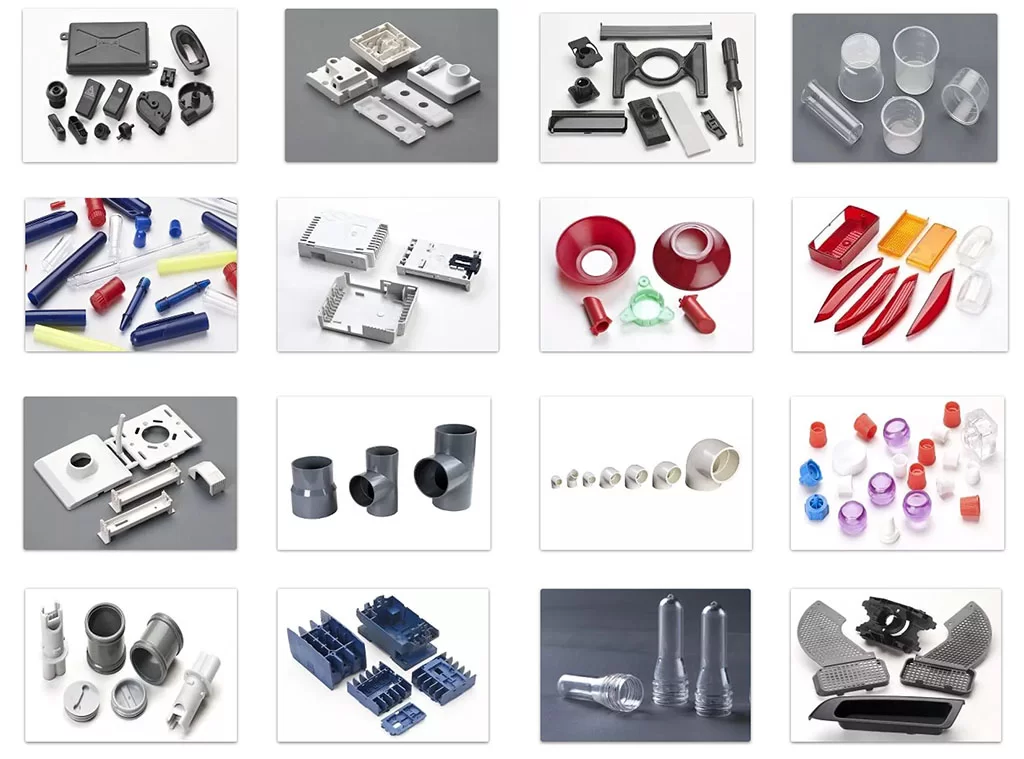

Plastic injection molding is widely used in various industries due to its ability to produce complex shapes, high-precision parts, and large quantities efficiently. Some key applications include:
- Automotive Industry:
- Components such as bumpers, dashboards, interior trim, and exterior body parts.
- Electronics Industry:
- Housings for electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, computers, and other consumer electronics.
- Medical Industry:
- Medical devices, disposable syringes, and other medical components.
- Consumer Goods:
- Toys, household appliances, furniture, and other consumer products.
- Packaging Industry:
- Plastic containers, bottles, and other packaging materials.
Additional Considerations
- Material Selection:
- The choice of plastic material depends on the specific application requirements, such as strength, durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals or heat.
- Mold Design:
- The design of the mold is critical to the success of the injection molding process. It must be able to withstand the pressures and temperatures involved and produce parts with the desired shape, size, and finish.
- Process Control:
- Close monitoring and control of the injection molding process parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and time, are essential to ensure consistent product quality.
In summary, plastic injection molding is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process that has a wide range of applications across multiple industries. By understanding its basics and carefully controlling the process parameters, manufacturers can produce high-quality plastic parts and products in large quantities.